A bowl of nutritious oatmeal is a daily fare for breakfast in many households around the world. It is made by boiling oats in either water or milk and adding fruits or sugar as desired. Unfortunately, some people find it difficult to digest oats. So what are the symptoms of oat intolerance? Read on to find out.
What Are Oats?

Oats are a type of whole grain from a plant scientifically known as Avena sativa, which belongs to the Poaceae grass family. Oats are considered to be one of the hardiest of cereals as they can adjust to a wide range of soil types. However, it is less tolerant of variations in climate. The plant thrives during the cool season but ceases to grow in hot weather. It originally came from Asia Minor but can now be found in most of Europe and parts of the US.
Nutrition Facts Of Oats

Oats are a cereal usually eaten in the form of oatmeal or rolled oats. It has a well-balanced nutrient composition being high in important vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Here is the nutritional value for a half cup or 40 grams of Great Value Old Fashioned Oats based upon the percentage daily value (DV) of the recommended 2000 calories per day diet.
Calories 150
Total Fat 2.5g (3%)
Cholesterol 0mg (0%)
Sodium 0mg (0%)
Total Carbohydrate 27g (10%)
Dietary Fiber 4g (14%)
Total Sugars 0g (0%)
Protein 5g
Vitamin D 0mcg (0%)
Iron 1.7mg (10%)
Calcium 20mg (0%)
Potassium 140mg (2%)
A half-cup of oats contains around 150 calories and 4 grams of dietary fiber, composed mostly of beta glucan. The recommended daily intake of fiber for women is 25 grams and 38 grams for men. Oats are a good source of protein and have more protein than most grains.
Health Benefits Of Eating Oats

Oats are chock-full of nutrients and are among the healthiest grains in existence. For the past several decades, oat consumption has continued to increase due to its many health benefits such as:
- Incredibly nutritious
- Rich in antioxidants
- Helps lower cholesterol levels
- Improves blood sugar control
- Reduces risk of cardiovascular disease
- Keeps you feeling full longer
- Helps relieve constipation
- Prevents the development of Type 2 Diabetes
- Mostly gluten-free
- Boosts the immune system
- Promotes good bacteria in the gut
- Helps to relieve skin irritation
Oat Intolerance vs. Oat Allergy
Food allergies affect around 1% of adults and 7% of children. Often, children tend to outgrow their allergies. On the other hand, food intolerances are much more prevalent.
Food intolerance pertains to problems with the digestive system. Oat intolerance is basically the inability to properly digest oats. So how will you know that you have this condition? Further down this article, we will be enumerating the symptoms of oat intolerance.
On the other hand, food allergy is an immune system reaction to a type of food, which in this case is oats. The symptoms of oat allergy include those of oat intolerance with the addition of a few more. There is no cure for oat allergy but it can be managed with the help of an allergy specialist or allergist.
Symptoms Of Oat Intolerance
After eating oats, a person can sometimes feel sick and manifest symptoms of oat allergy. However, it can also be due to gluten intolerance. People with gluten intolerance and its serious form called celiac disease should exercise caution when consuming foods containing gluten or avoid it altogether.
Oats do not contain gluten, but cross-contamination can occur when it is grown in a field or processed in facilities at the same time as other crops that contain gluten such as wheat, barley, and rye. This can lead to a misdiagnosis of the true condition.
Oat intolerance is not life-threatening. Symptoms after oat consumption range from mild to severe and often take longer to occur. However, these symptoms can become chronic if you continue to eat oats repeatedly and they include:
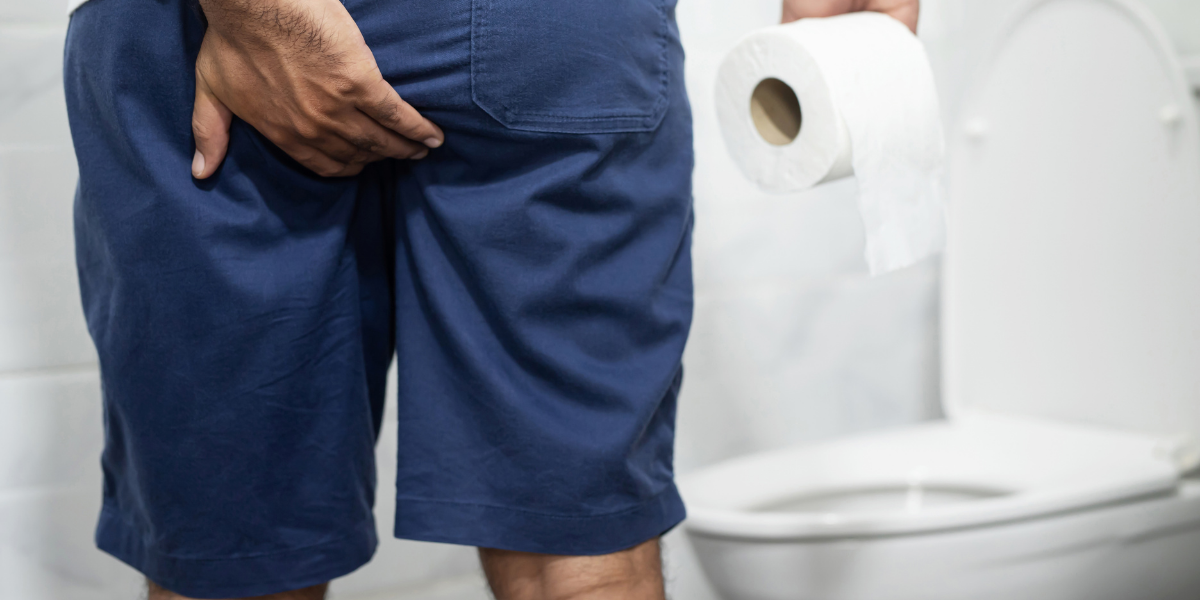

-
Diarrhea
Oats are high in both soluble and insoluble fiber. Unfortunately, insoluble fiber often causes diarrhea when too much of it has been consumed. Insoluble fiber attracts water which is then absorbed into the stool in the gastrointestinal tract. This leads to the formation of loose watery stool known as diarrhea.
Getting diarrhea from eating oats should not be a cause for concern as it can easily be remedied by a change in diet. A healthy balance of soluble and insoluble fiber should help solve bowel movement problems, both with diarrhea and constipation.

-
Nausea and vomiting
If you are overly sensitive to high-fiber foods, you may experience gastric upset when consuming oats. This may lead to episodes of nausea and vomiting as well as all the other symptoms.
Another reason for these symptoms is a protein called avenin which amounts to 80% of the total protein content in oats and is not found in any of the other grains. Avenin can cause an allergic reaction in some people so don’t be alarmed if you suddenly feel ill and throw up after eating oatmeal. Avoiding foods containing oats or consuming them in small amounts should do the trick.
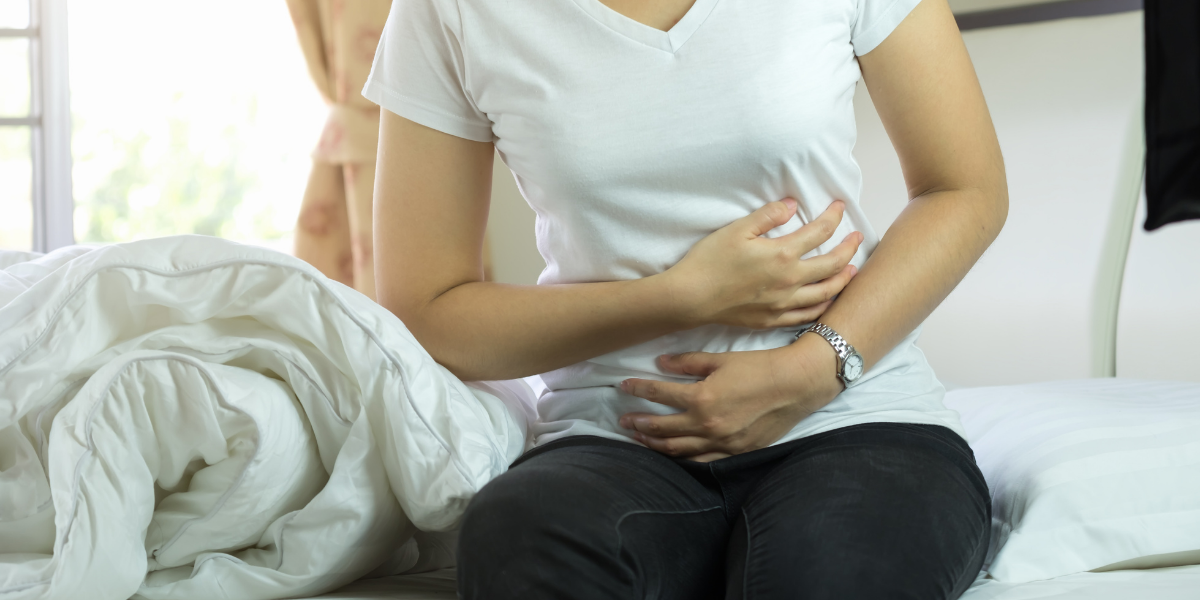

-
Stomach pain
People suffering from disorders of the digestive tract such as the esophagus, stomach, and intestines should avoid eating oat products. In cases when the condition delays the time it takes for food to be digested, oats can temporarily block the intestine. This can cause uncomfortable stomach issues such as gastric pain.

-
Gas and bloating
Oat bran and whole oats may be safe to be eaten in foods for most people but oats can bring about not-so-pleasant experiences to a few others. The culprit, in this case, is beta glucan, a type of fiber that is abundant in oats. Like all sources of fiber, beta glucan may cause gastric discomfort, gas, and bloating when ingested in large amounts.
According to a published article by gastroenterologist Dr. Jennifer Bonheur in Bonheur MD, when you start eating whole-grain cereals such as oatmeal and oat bran, you may feel bloated due to the high-fiber diet that you are not yet accustomed to. To minimize these side effects, it is best to start consuming oats in small amounts and gradually increasing to the desired amount. As your body begins to get used to the oats, the side effects may disappear altogether–or it may not.
Oat Allergy is More Dangerous!

While oat intolerance manifests mostly through problems with digestion, oat allergies are apparent not only through gastrointestinal symptoms but also through skin reactions, respiratory difficulties, and worst of all, anaphylaxis. Therefore, oat allergies can exhibit all of the symptoms of oat intolerance mentioned earlier with significant additions like:
- Irritated or itchy skin
- Mild swelling of the face, lip, or eyes
- Red, itchy rash on the mouth, tongue, or eyes
- Flushed face
- Clogged or runny nose
- Breathing difficulties
- Itchy throat
- Itchy or watery eyes
- Anaphylaxis
The Dangers Of Anaphylaxis

Oat allergy is rare but it does happen. If you are extremely allergic to oats, it can lead to anaphylactic shock which can be fatal if not treated immediately. Thus the need to discuss it a bit more.
Anaphylaxis is a dangerous reaction that occurs when people who have severe allergies to a certain food, medication, or substance are suddenly exposed to their allergen.
A diagnosis of anaphylaxis can follow symptoms such as::
- Mental Confusion
- Rapid or abnormal heart rate
- Weakness or dizziness
- Low blood pressure
- Facial swelling
- Throat swelling
- Wheezing
- Hives
- Blue skin
The immune system overreacts to the oats and turns into a full-body allergic reaction. It can even cause you to stop breathing or block your airway due to inflammation, cause your blood pressure to drop, and may even provoke a heart attack.
Once diagnosed, your doctor will probably request you to bring a medication called epinephrine with you all the time. Epinephrine can prevent future allergic reactions from becoming life-threatening.
Oat Sensitivity In Children
Oat allergy can also happen to babies and small children. Due to their small size and inability to express themselves clearly, it is particularly important to pay close attention to the appearance of any of these manifestations.:
-
Food protein-induced enterocolitis (FPIES)
Most symptoms of allergy appear shortly after ingesting the allergen. But sometimes, it may take 4 to 6 hours or even longer before symptoms appear. One example of this delayed food allergy reaction is food protein-induced enterocolitis (FPIES) which involves the gastrointestinal tract. A lot of foods and not just oats can trigger FPIES.
Often, babies trying out certain foods for the first time or undergoing weaning have the highest tendency to be affected by FPIES. The severe gastrointestinal symptoms such as frequent vomiting, bloody diarrhea, and dehydration manifest within 2 to 6 hours after exposure to the allergen. When allowed to continue for the long term, they can fall into lethargy and malnutrition. Infants exhibiting symptoms of FPIES need immediate medical intervention.
-
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition that shows dry, itchy and inflamed areas on the skin. The condition is brought about when a person’s immune system goes into overdrive upon exposure to an allergen. There is no cure for atopic dermatitis and it tends to flare up periodically.
Oat allergy can also manifest when applied directly to the skin. A 2007 study on 302 children revealed that a significant number of them showed allergic skin reactions to products containing oats such as baths and lotions. Results on subjects with atopic dermatitis showed that oat sensitization was higher than expected.
Foods To Avoid

If you have sensitivity to avenin, you should eliminate oats and oat products from your diet. Always watch out for the words oats, oat powder, and avenin on the labels. Here are some foods that contain these ingredients:
- Oatmeal
- Oatmeal cookies
- Granola and granola bars
- Porridge
- Oatcake
- Flapjacks
- Muesli
- Oat milk
- Oat beers
How To Test For Oat Sensitivity
There are several ways to test for oat sensitivity, as well as to other types of food. In order to be sure of the diagnosis, an allergist can test you for oat allergy. Here are some of the methods:
-
Oral Food Test
This test requires you to eat small amounts of oats that are gradually increased under close monitoring. As soon as the allergist notices some signs of adverse reaction, the test will be immediately stopped. If you show no reaction at all, then the oats can be safely ruled out as the cause. The oral food test must always be done in a medical facility so that any severe allergic symptoms that occur can be treated on-site.
-
Skin Prick Test
An allergist will prick the skin of your forearm with a small amount of diluted oats along with histamine, saline, or glycerin to see if it generates an allergic response. This test can also gauge your allergic reaction to various substances at once. It is not painful and results can be achieved after around 20 to 40 minutes.
-
Patch Test
In this test, the allergist applies small amounts of oats on patches that should remain stuck to your arm or back for up to 48 hours to check in case you have any delayed allergic reactions to the oats.
-
Elimination Diet
The elimination diet is usually recommended for children to test for allergens. It involves removing all foods containing oats from the diet for one week and regularly checking the symptoms if they improve. If a marked improvement is noted, then chances are that the child is allergic to oats.
Oat Alternatives
Oat is high in fiber, in particular, the soluble fiber beta-glucan which helps in lowering cholesterol levels and minimizes the risk of heart disease. If you happen to have oat intolerance, some other cereals and grains can replace oats in your diet and they include:
- Brown rice
- Corn
- Sorghum
- Quinoa
- Millet
- Polenta
- Buckwheat
Takeaway

Intolerance or allergy to oats is uncommon but can be life-threatening. They arise from sensitivity to chemical compounds, such as protein, that are found in oats. Exposure to a food protein that your body perceives as harmful, such as avenin in oats, can cause you to develop oat intolerance or oat allergy.
Oat intolerance is treated by eliminating or reducing your intake of the problem food which, in this case, is oats. In addition, immediate treatment of the symptoms the moment they appear should be done.
If you experience several of the symptoms mentioned above and suspect that you may have oat intolerance or oat allergy, you need to consult a doctor or an allergist as soon as possible. For now, the first step is to be aware what the symptoms of oat intolerance and oat allergy are so you can identify them and take the necessary measures.

